A Practical, Expert Guide to Comfort, Support, and Health
After sitting at a desk for a few hours, most people feel it.
Your back tightens, your lower spine feels compressed, and instinctively, you lean back, hoping your chair will give you a bit of relief.
When adjusted correctly, an office chair recline does far more than feel comfortable for a moment. It helps reduce spinal pressure, supports natural posture changes, and gives your body a chance to recover during the workday. When adjusted incorrectly, however, reclining can actually increase strain on your lower back and neck.
So the real question is:
How do you adjust an office chair recline the right way?
This guide explains the process step by step, based on real-world experience in office furniture design, workspace planning, and ergonomic seating, not theory.
Why Proper Recline Adjustment Matters More Than You Think
From an ergonomic standpoint, sitting upright for long periods places constant pressure on the spine. A properly adjusted office chair recline angle allows your body to shift positions while staying supported.
Used correctly, reclining can:
- Reduce pressure on the lumbar spine
- Ease back and shoulder fatigue
- Improve circulation during long work sessions
- Increase comfort and focus throughout the day
That’s why almost every ergonomic office chair includes a recline function. The problem is that many people never adjust it correctly or never use it at all.
Step 1: Understand Your Office Chair Before You Adjust It
Before touching any knobs or levers, take a moment to understand what kind of chair you’re using.
Different office chair models and brands use different recline mechanisms. The most common include:
- Knob-controlled recline locks
- Lever-controlled recline systems
- Synchronous tilt mechanisms
- Multi-position recline locking systems
Most office chair recline controls are located under the seat, usually as one or two knobs or levers.
Expert tip: Many recline problems happen because people adjust the wrong control first. Take a second to identify what each part actually does.
Step 2: Locate the Recline Control Knob or Lever
Under your chair, you’ll typically find:
- A round tension or lock knob, often used to control recline angle or resistance
- A control lever, commonly used for seat height and sometimes recline unlocking
If your chair supports reclining, you’ll often see a tilt or angle icon near the control.
Be careful not to confuse the seat height lever with the recline control. This is one of the most common mistakes users make.
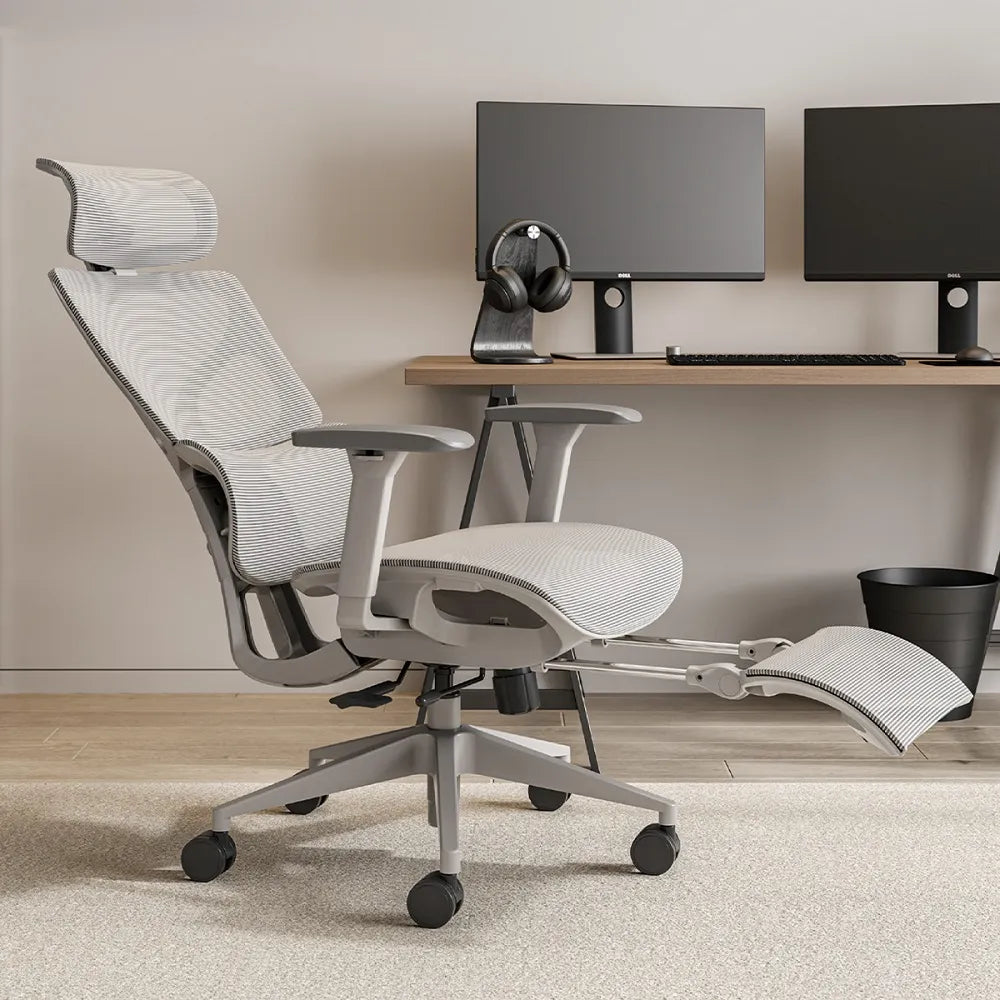
Step 3: How to Adjust the Office Chair Recline Angle Correctly
Once you’ve identified the correct control, follow this safe and effective process:
1. Unlock the Recline Function
- Knob-based chairs: Turn the knob counterclockwise to unlock
- Lever-based chairs: Pull the lever out or lower it to enable reclining
2. Lean Back Slowly
Keep your feet flat on the floor and lean back using your body weight. Let the chair recline naturally until your back feels fully supported.
3. Lock the Recline Angle
Once you find a comfortable position:
- Turn the knob clockwise to lock
- Or return the lever to its original position
If your chair uses a synchronous tilt mechanism, the movement should feel smooth, with your back reclining more than the seat.
Step 4: Test Comfort and Fine-Tune the Position
After locking the recline, stay seated for at least a few minutes and pay attention to how your body feels.
Check for these signs:
- Your lower back feels supported, not hanging
- Your back stays in contact with the backrest
- Your neck and shoulders feel relaxed
- The recline feels stable, not jerky or loose
If something feels off, make small adjustments. Recline works best when combined with proper lumbar support, seat depth, and armrest height.
Professional insight: The best office chair recline angle isn’t extreme. It’s the one that supports your body without making you think about it.
Different Office Chair Recline Mechanisms Explained
Why Some Chairs Feel Better Than Others
Many people ask why one chair reclines comfortably while another feels awkward or tiring. The answer lies in the recline mechanism.
1. Basic Recline Mechanism (Single-Point Tilt)
Best for short-term or occasional use
The seat and backrest tilt together as one unit.
Pros:
- Simple and easy to use
- Common in basic office chairs
Cons:
- Can lift the thighs when reclining
- Limited support for long sitting hours
2. Synchronous Tilt Mechanism
The gold standard for ergonomic office chairs
The backrest reclines more than the seat, keeping your body balanced and supported.
Pros:
- Reduces pressure on the lower back
- Natural reclining motion
- Ideal for long workdays
3. Multi-Position Recline Lock
Designed for posture control and stability
Allows the backrest to lock at several fixed angles.
Pros:
- Stable and predictable
- Common in corporate and government offices
Cons:
-
Less flexible for frequent movement
4. Weight-Sensitive Recline (Auto-Adjusting Tilt)
High-end comfort with minimal adjustment
Automatically adjusts recline resistance based on body weight.
Pros:
- Smooth and effortless
- No constant manual adjustments
Cons:
- Higher cost
Often found in premium executive or high-performance ergonomic office chairs.
How Reclining Affects Long-Term Health
When used properly, an office chair recline function helps:
- Lower spinal disc pressure
- Reduce chronic back discomfort
- Improve posture changes during the day
- Support healthy movement while seated
For people who sit for long hours, including remote workers, designers, programmers, and office professionals, recline isn’t optional. It’s essential.
Final Thoughts: Make Your Office Chair Work for You
A good office chair isn’t just something you sit on. It’s something that supports you through hours of focused work.
Once you understand how to adjust an office chair recline, recognize different recline mechanisms, and fine-tune the angle for your body, even a standard chair can feel dramatically better.
Used correctly, your chair becomes a tool for comfort, productivity, and long-term spinal health.
Read more: Everything you need to know about how office chair height adjustment works.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the best recline angle for an office chair during work?
For most people, the best office chair recline angle for daily work falls between 100° and 110°. This range allows your back to stay supported while reducing pressure on the lower spine. For short breaks or reading, a slightly deeper recline can feel relaxing, but extreme angles are not recommended for long periods of focused work.
2. Should I lock my office chair recline or leave it free-moving?
It depends on how you work. If you tend to change positions often, leaving the office chair recline free-moving with proper tension can feel more natural. If you prefer stability while typing or attending meetings, locking the recline at a comfortable angle usually provides better posture control and consistency throughout the day.
3. Why does my office chair feel uncomfortable when I recline?
Discomfort while reclining is usually caused by one of three issues:
an incorrect recline angle, insufficient lumbar support, or a basic recline mechanism that doesn’t support natural body movement. Chairs with synchronous tilt mechanisms generally provide better support and feel more balanced when reclining for longer periods.
4. Is reclining in an office chair good for your back?
Yes, when done correctly. Using the office chair recline function helps reduce spinal compression and allows your back muscles to relax. The key is to recline just enough to stay supported, not so far that your lower back loses contact with the backrest. Proper reclining is especially helpful for people who sit for long hours at a desk.
5. How do I know if my office chair has a good recline mechanism?
A quality recline mechanism should feel smooth, controlled, and stable. When you lean back, the chair should support your body without sudden drops or resistance. In the US market, ergonomic office chairs with synchronous or weight-sensitive recline systems are widely considered the best options for long-term comfort and spinal health.
Further reading
Occupational Safety and Health Administration. (n.d.). Computer Workstations eTool: Ergonomic guidelines.
U.S. Department of Labor.
https://www.osha.gov/etools/computer-workstations
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. (2015). Elements of ergonomics programs: Musculoskeletal disorders and workplace factors.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/97-117/
Hedge, A. (2016). Office ergonomics: Practical guidelines for chair adjustment and posture.
Cornell University Ergonomics Web.
https://ergo.human.cornell.edu/ergoguide.html
American Chiropractic Association. (2021). Sitting posture and spinal health.
American Chiropractic Association.
https://www.acatoday.org/news-publications/posture-and-spinal-health/









Deixar comentário
Os comentários precisam ser aprovados antes da publicação.
Este site é protegido por hCaptcha e a Política de privacidade e os Termos de serviço do hCaptcha se aplicam.